Ankle injuries can be a daunting setback for athletes and active individuals, but understanding the nuances of recovery can make a significant difference. One often-overlooked aspect of ankle sprain assessment is the role of the retinaculum, a key player in proprioception and stability. This connective tissue structure is essential for maintaining balance and preventing further injury, making it a critical focus during rehabilitation. As we explore the importance of the retinaculum, you’ll discover techniques for rehabilitating ankle sprains that emphasize proprioception in ankle injuries, laying the groundwork for effective recovery. Whether you’re a dedicated athlete or simply looking to regain your stride, this guide aims to support your journey toward healing and ankle injury prevention.
Understanding Ankle Sprain Assessment
Proper assessment of ankle sprains is vital for effective treatment and recovery. This section delves into the key aspects of evaluating ankle injuries, with a focus on the often-overlooked retinaculum.
Assessing the Severity of Ankle Injuries
Ankle sprain assessment begins with a thorough examination of the injury site. Physical therapists and healthcare professionals typically follow a structured approach to determine the extent of damage.
The assessment generally starts with a visual inspection, checking for swelling, bruising, and deformity. This is followed by gentle palpation to identify areas of tenderness and potential ligament damage.
Range of motion tests and stress tests are subsequently performed to evaluate the stability of the ankle joint. These tests help categorize the sprain into grades of severity, which guide treatment decisions.
Imaging studies, such as X-rays or MRI scans, might be necessary in some cases to rule out fractures or assess soft tissue damage more precisely.
Importance of Retinaculum in Evaluation
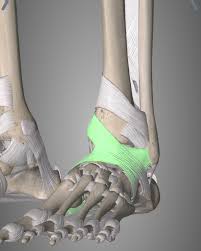
The retinaculum, a band of connective tissue that helps stabilize tendons around the ankle, plays a critical role in ankle function and stability. Its assessment is often overlooked but is crucial for a comprehensive evaluation.
During the examination, healthcare providers should closely examine the integrity of the retinaculum. This involves palpating the area around the ankle to detect any abnormalities or instability in the retinacular structures.
Specific tests, such as the peroneal tendon subluxation test, can help evaluate the condition of the retinaculum. These tests involve manipulating the foot and ankle to assess the stability and function of the retinacular structures.
Including retinaculum assessment in ankle sprain evaluation can lead to more accurate diagnoses and targeted treatment plans, ultimately enhancing recovery outcomes.
The Role of Proprioception in Ankle Injuries
Proprioception, our body’s ability to sense position and movement, is crucial in maintaining balance and preventing injuries. This section examines how the retinaculum influences proprioception and its importance in ankle injury recovery.
How Retinaculum Affects Proprioception
The retinaculum plays a significant role in ankle proprioception, acting as a sensory organ that provides crucial feedback about ankle position and movement.
This connective tissue contains numerous mechanoreceptors, which are sensory nerve endings that detect changes in tension, pressure, and movement. These receptors send signals to the brain, allowing for rapid adjustments in muscle activity and joint position.
When the retinaculum is damaged, proprioceptive function can be impaired, leading to decreased balance and an increased risk of re-injury. This underscores the importance of addressing retinacular health in ankle injury rehabilitation.
Understanding the relationship between the retinaculum and proprioception can guide more effective treatment strategies, focusing on restoring not just strength and flexibility, but also sensory function.
Enhancing Proprioception During Recovery
Improving proprioception is a key component of ankle injury rehabilitation. This process involves specific exercises and techniques designed to retrain the body’s sense of position and movement.
Balance exercises are fundamental in proprioceptive training. These can range from simple single-leg stands to more complex activities using unstable surfaces like balance boards or foam pads.
Progressive difficulty in exercises is crucial. As balance improves, exercises can be made more challenging by adding movements, closing eyes, or incorporating sports-specific actions.
Neuromuscular training, which combines balance, strength, and agility exercises, has shown significant benefits in improving proprioception and reducing the risk of re-injury.
Consistent practice and patience are essential, as proprioceptive improvements typically occur gradually over several weeks of dedicated training.
Rehabilitating Ankle Sprains Effectively
Effective rehabilitation of ankle sprains involves a comprehensive approach that addresses all aspects of ankle function, including strength, flexibility, and proprioception. This section outlines key strategies for recovery and injury prevention.
Key Strategies for Ankle Injury Prevention
Preventing ankle injuries is crucial for maintaining long-term ankle health and avoiding the setbacks associated with sprains. A multi-faceted approach yields the best results.
Regular strengthening exercises for the ankle and lower leg muscles help improve stability and resilience. This includes exercises targeting the calf muscles, peroneal muscles, and tibialis anterior.
Flexibility training is equally important. Regular stretching of the calf muscles, Achilles tendon, and other ankle structures can improve range of motion and reduce injury risk.
Proprioceptive training, as discussed earlier, should be incorporated into regular workout routines, even for those without a history of ankle injuries.
Proper footwear selection and the use of supportive devices like ankle braces during high-risk activities can provide additional protection against sprains.
Techniques for Strengthening the Retinaculum
Strengthening the retinaculum is an often-overlooked but crucial aspect of ankle rehabilitation and injury prevention. Specific exercises can help improve the function and resilience of this important structure.
Resistance band exercises are particularly effective. These include eversion exercises where the foot is moved outward against the resistance of the band, targeting the peroneal muscles and associated retinaculum.
Proprioceptive exercises that challenge balance and stability also help strengthen the retinaculum indirectly by improving overall ankle function and control.
Manual therapy techniques performed by a skilled therapist can help improve the flexibility and function of the retinaculum, complementing strengthening exercises.
Consistent practice and gradual progression in exercise difficulty are key to effectively strengthening the retinaculum and improving overall ankle stability.
Summary
In conclusion, understanding and addressing the role of the retinaculum in ankle injury recovery is pivotal in achieving optimal results. This often-overlooked structure plays a critical part in proprioception and stability, both of which are essential for effective rehabilitation. Through targeted assessment and specialized rehabilitation techniques that include strengthening and proprioceptive exercises, individuals can enhance their recovery outcomes significantly. By integrating these strategies into rehabilitation programs, athletes and active individuals can not only expedite their healing process but also prevent future injuries, enabling them to maintain an active lifestyle with confidence